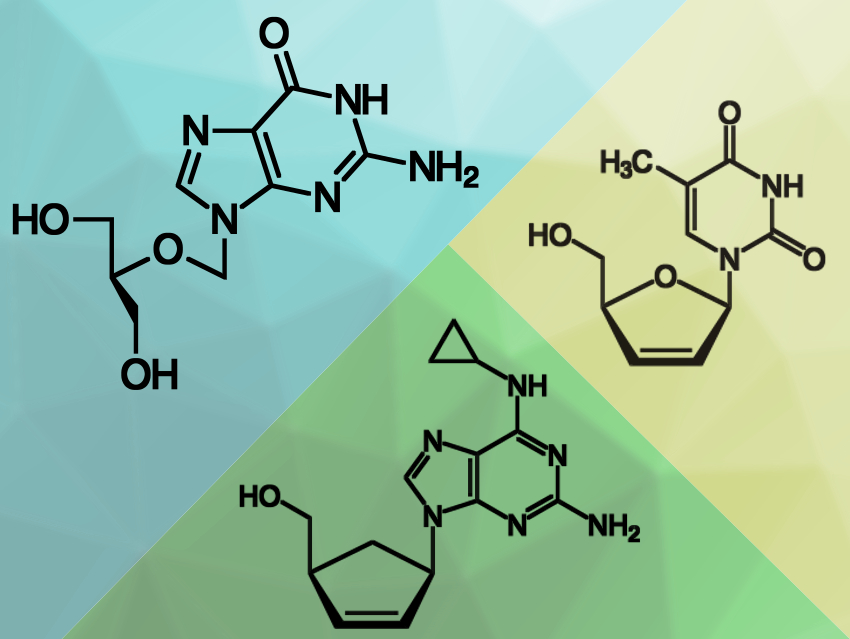
The worldwide outbreak of the respiratory disease COVID-19 is caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. To multiply, the virus has to copy its genetic material inside a host cell. This process is performed by an enzyme, the virus’s RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). Drugs that disrupt this replication process could be useful to treat COVID-19. Certain nucleotide analogues (examples pictured) can be used for this. These analogues are compounds that are structurally similar to the usual substrates of the enzyme, but chemically modified either at the sugar unit or the nucleobase.
Robert N. Kirchdoerfer, University of Wisconsin-Madison, USA, Jingyue Ju, Columbia University, New York, USA, and colleagues have tested eleven different nucleotide analogues as inhibitors of the polymerases of SARS-CoV-2. The team performed polymerase extension assays with these analogues, either alone or in combination with natural nucleotides. The reaction products were analyzed using MALDI–TOF (matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization–time-of-flight) mass spectrometry.
The team found that six of the tested molecules showed immediate termination of the polymerase reaction, namely the triphosphates of Carbovir, Ganciclovir, Stavudine, and Entecavir, as well as 3′-O-methyluridine-5′-triphosphate (3′-OMe-UTP), and biotin-16-aminoallyl-2′-deoxyuridine-5′-triphosphate (Biotin-16-dUTP). An additional two compounds showed a delayed termination of the polymerase reaction: Cidofovir diphosphate and 2′-O-methyluridine-5′-triphosphate (2′-OMe-UTP).
For five of these active candidates, there are already nucleotide prodrugs that are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). These prodrugs are used to treat other viral infections, such as HIV/AIDS, cytomegalovirus, or hepatitis B. According to the researchers, the results provide a basis for further evaluation of these prodrugs for the development of COVID-19 therapeutics.
- A library of nucleotide analogues terminate RNA synthesis catalyzed by polymerases of coronaviruses that cause SARS and COVID-19,
Steffen Jockusch, Chuanjuan Tao, Xiaoxu Li, Thomas K. Anderson, Minchen Chien, Shiv Kumar, James J. Russo, Robert N. Kirchdoerfer, Jingyue Ju,
Antiviral Res. 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104857
Also of Interest
- Collection: SARS-CoV-2 Virus
What we know about the new coronavirus and COVID-19 - LitCovid
Curated literature hub for tracking up-to-date scientific information about COVID-19 - Many publishers and other entities have signed a joint statement to ensure that COVID-19 research findings and data are shared rapidly and openly