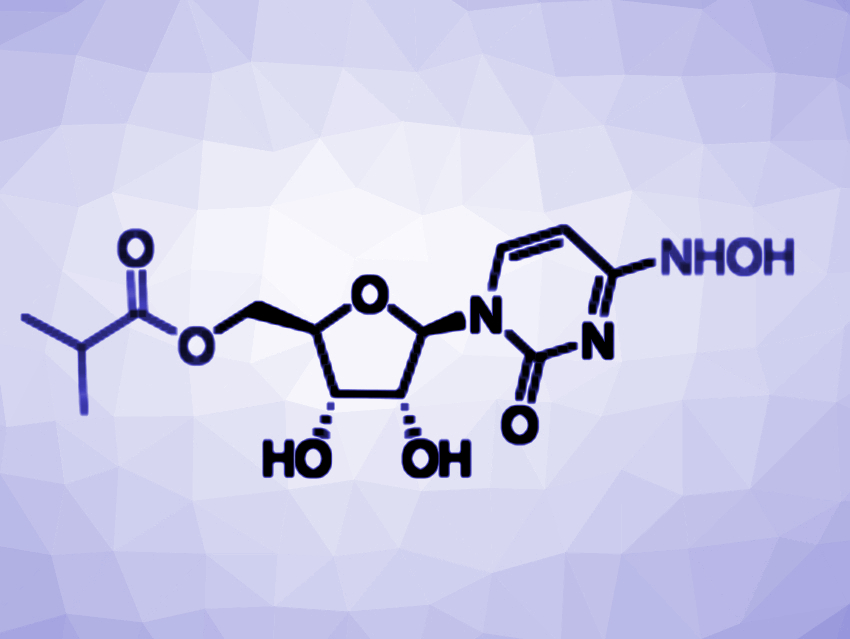
The COVID-19 pandemic is caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Drugs for the treatment of this disease are urgently needed. The antiviral compound EIDD-2801 (also called molnupiravir or MK-4482, pictured) is a potential drug candidate against COVID-19 and is currently in phase II/III clinical trials. The drug has been repurposed—originally, it was designed as a ribonucleoside analogue inhibitor of influenza viruses.
Richard K. Plemper, Georgia State University, Atlanta, USA, and colleagues have found that EIDD-2801 can reduce the viral load in the upper respiratory tract and suppress virus transmission in ferrets. The team considers ferrets a good model because the animals can readily spread the virus, but generally do not develop severe disease—similar to young human adults. The team infected ferrets with SARS-CoV-2 and started treatment with EIDD-2801 when the animals began to shed virus from the nose. The infected, treated animals were co-housed with healthy, untreated ferrets in the same cage. None of these contact animals became infected. In a control experiment, all contacts of infected, untreated ferrets became infected.
In contrast to other possible COVID-19 treatments such as remdesivir or convalescent serum, EIDD-2801 can be given orally. This could significantly simplify treatment and transmission prevention. According to the researchers, the drug could possibly help to prevent widespread community transmission of COVID-19 until vaccinations are widely available.
- Therapeutically administered ribonucleoside analogue MK-4482/EIDD-2801 blocks SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets,
Robert M. Cox, Josef D. Wolf, Richard K. Plemper,
Nat. Microbiol. 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-020-00835-2
Also of Interest
- Collection: SARS-CoV-2 Virus
What we know about the new coronavirus and COVID-19
News: Coronavirus Drug Molnupiravir
- 05 October 2021
Molnupiravir significantly reduces risk of hospitalization and/or death, according to Merck
News: Improved Synthesis Route for Molnupiravir
- 04 August 2021
Efficient synthesis from cheap and easily available cytidine
Research Highlight: How Molnupiravir Causes SARS-CoV-2 to Mutate and Die
Mechanism might apply to various viral polymerases and could explain broad-spectrum antiviral activity of molnupiravir
News: High-Yielding Synthesis of Antiviral Drug Candidate
- 19 November 2020
Improved preparation of EIDD‐2801, currently in clinical trials for COVID-19 treatment
News: Oral Drug Blocks SARS-CoV-2 Transmission in Ferrets
- 09 December 2020
Repurposed ribonucleoside analogue inhibitor of influenza viruses