Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) is a semisynthetic hallucinogenic drug. It was first synthesized November 16, 1938, by Albert Hofmann as a potential circulatory and respiratory stimulant for a research project into the medicinal properties of ergot alkaloids. As this compound appeared to have no interesting effects when tested on animals, it wasn’t initially further investigated.
It was not until five years after the first synthesis that Albert Hofmann discovered the psychopharmacological effects of LSD when he accidently absorbed a small quantity of the compound through his fingertips and experienced unusual sensations. He then deliberately ingested 0.25 mg and discovered that the effects were a lot stronger than he had expected. A research project was carried out and Sandoz Laboratories, Basel, Switzerland, introduced LSD as an experimental drug in 1947. It was used in experiments by psychiatrists throughout the 1940s, 1950s, and 1960s. Its subsequent recreational use led to it being prohibited in the western world in the 1960’s.
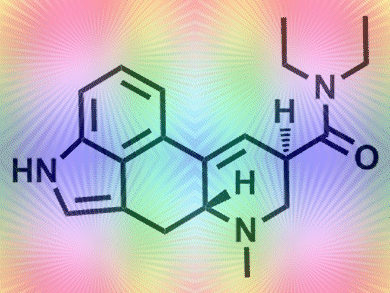
LSD is an amide derivative of lysergic acid, derived from ergot alkaloids. Hofmann synthesized LSD using the Curtius synthesis, in which diethylamine is coupled with lysergic acid in the presence of the activating agent phosphoryl chloride. It contains stereogenic centers at the C5- and C8-positions and the active form, (+)-LSD (find out more here), has the absolute configuration 5R, 8R.
Albert Hofmann is the answer to Guess the Chemist (23), which gave details about Hofman’s life.
Source
- LSD – My Problem Child: Reflections on Sacred Drugs, Mysticism and Science,
Albert Hofmann,
Multidisciplinary Association for Pschedelic Studies (MAPS), Santa Cruz, USA, 2009.
ISBN: 978-0979862229
Also of Interest

The isolation and structural determination of the potent ergot alkaloids guarantees we can enjoy our daily bread without harm

What is an ergot-infested grain kernel? Part 2 looks at the life-cycle of the fungus, how it contributed to the Salem witch trials, and a self test

The Isenheim Altar depicts the symptoms and treatment of “St. Anthony’s Fire”, the result of poisoning by ergot alkaloids

A growing collection of articles looking at substances like nicotine, LSD, and marijuana from a chemical perspective, exploring how they are used and why, etc.